Buffer Salt Chemistry Definition
Epsom salt magnesium sulfate. Tris also complexes with metal ions in solution.
 2012 Topic 18 2 Buffer Solutions
2012 Topic 18 2 Buffer Solutions
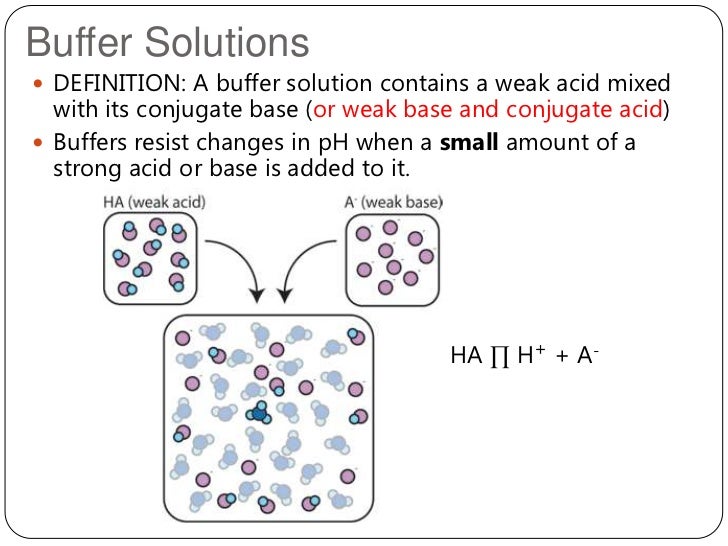
A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH.

Buffer salt chemistry definition. Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. A buffer is a solution that can maintain a nearly constant pH if it is diluted or if relatively small amounts of strong acids or bases are added. Definition A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it.
Mixture of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and Sodium acetate CH 3 COONa in water. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base. Buffers are broadly divided into two types acidic and alkaline buffer solutions.
An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. Updated May 04 2019. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
You can explore more about buffer solutions here. Weak acid and its conjugate base d. Buffers can be prepared from any a.
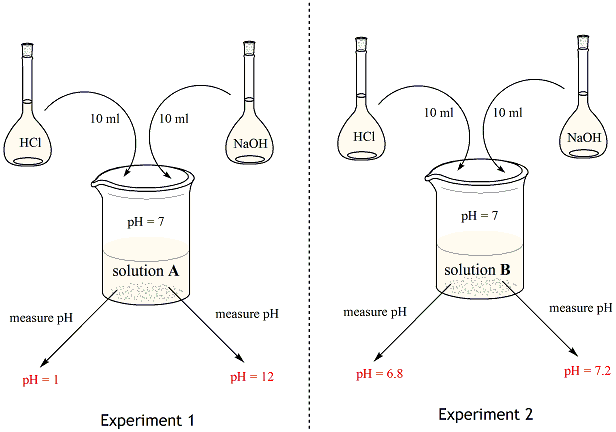
Salt and acid b. A buffer or buffered solution is one that resists a change in its pH when H or OH ions are added or removed owing to some other reaction taking place in the same solution. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications.
Buffer salt a salt in the blood that is able to absorb slight excesses of acid or alkali with little or no change in the hydrogen ion concentration. There are two key terms associated with buffers. Glaubers salt sodium sulfate.
Similarly adding water to a buffer or allowing water to evaporate will not change the pH of a buffer. In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions. Direct link to Melody Tans post A buffer solution is a solution that only changes.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. Either a weak acid plus a salt derived from that weak acid or a weak base plus a salt of that weak base. Either a weak acid plus its conjugate base or a weak base plus its conjugate acid.
Anne Marie Helmenstine PhD. Furthermore it consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice-versa. A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components.
It is extensively used in biochemistry and molecular biology as a component of buffer solutions such as in TAE and TBE buffers especially for solutions of nucleic acids. In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. A buffer solution refers to an aqueous solution.
If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. For an acid-buffer solution it consists of a week acid and its conjugate base. Buffers do so by being composed of certain pairs of solutes.
This solution is quite important in the field of chemistry. Base and its conjugate acid c. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood.
Buffers do so by being composed of certain pairs of solutes. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. It contains a primary amine and thus undergoes the reactions associated with typical amines eg.
A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. How are Acid-Base Buffers Made. Acidic buffers are solutions that have a pH below 7 and contain a weak acid and one of its salts.
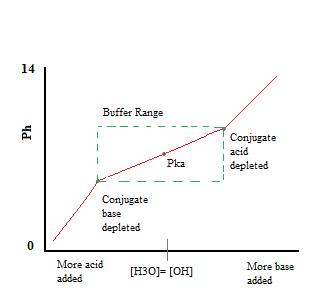
In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation. A buffer solution can be made by mixing a weak acid with one of its salts OR mixing a weak base with one of its salts. By definition a buffer system is a solution that resists a change in pH when acids or bases are added.
For example a buffer can be composed of dissolved HC 2 H 3 O 2 a weak acid and NaC 2 H 3 O 2 the salt derived from that weak acid. For example a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts as a buffer solution with a pH of about 475. A buffer solution is a solution that only changes slightly when an acid or a base is added to it.
The ion with a positive charge is called a cation and the one with a negative charge is. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. A solution which resists the change in its pH value even on the addition of a small amount of strong acid or base is called a buffer solution or buffer.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. Acidic solutions contain high concentrations of hydrogen ions H and have pH values less. Strong acid and its conjugate base.
What Is a Buffer. In chemistry a salt is an ionic compound which is made up of two groups of oppositely charged ions.
 Covalent Bond Animation Chemistry Covalent Bonding Bond Chemistry
Covalent Bond Animation Chemistry Covalent Bonding Bond Chemistry
 Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry
 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
 Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Chemistry Khan Academy Khan Academy Chemistry Henderson
Buffers And Henderson Hasselbalch Chemistry Khan Academy Khan Academy Chemistry Henderson
 Buffers Introductory Chemistry
Buffers Introductory Chemistry
 Electrolysis Of Molten Nacl Oxidation Half And Reduction Half Cell Reactions In Electrolytic Cell Oxidation Molten Cell
Electrolysis Of Molten Nacl Oxidation Half And Reduction Half Cell Reactions In Electrolytic Cell Oxidation Molten Cell
 Pin On Chemistry Acids And Bases
Pin On Chemistry Acids And Bases
 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
 Coordinate Covalent Bond Definition Examples Formation And Properties Covalent Bonding Coordinates Cool Websites
Coordinate Covalent Bond Definition Examples Formation And Properties Covalent Bonding Coordinates Cool Websites
 Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is The Difference Between Oxidation And Red Electrochemistry Oxidation State Oxidation
Digital Kemistry Best Chemistry Animated Blogs What Is The Difference Between Oxidation And Red Electrochemistry Oxidation State Oxidation
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
 Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Acidic Buffer Basic Buffer Animation Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
 Common Ion Effect Animation Chemistry Ionic Equilibrium
Common Ion Effect Animation Chemistry Ionic Equilibrium



